Effective filtration is the silent guardian of our appliances, culinary creations, and even industrial processes, preventing unwanted particles from compromising performance or purity. From the limescale catcher in your electric kettle to the grease trap in a range hood, filters play a crucial role in daily life. When it comes to choosing the right filtration solution, two terms often arise: mesh filters and stainless steel filters. While seemingly distinct, understanding their nuances and overlaps is key to making an informed decision for superior filtration. This guide delves into the characteristics, advantages, and ideal applications of both, helping you navigate the world of filters.

Understanding Filtration: The Basics
At its core, filtration is the process of separating solid particles from liquids or gases by passing the mixture through a filter medium that retains the solids. This fundamental principle ensures the cleanliness, safety, and efficiency of countless systems. Filters are designed with specific pore sizes and structures to capture particles ranging from microscopic impurities in drinking water to larger debris in industrial wastewater. The effectiveness of a filter is determined by its ability to trap contaminants while allowing the desired fluid or gas to pass through with minimal obstruction.
Exploring Mesh Filters: Structure and Function
Mesh filters are characterized by their intricate, woven or knitted structure, forming a network of uniform openings. This design allows for a clear passage of liquids or gases while trapping solid particles larger than the mesh apertures. The material used for mesh filters can vary widely, including plastics, aluminum, nylon, and most notably, stainless steel, each offering different performance characteristics.
For instance, plastic mesh filters are often found in basic household items due to their low cost and lightweight nature, suitable for less demanding applications. Nylon mesh, while capable of very fine filtration down to 60 microns, can be prone to tearing if exposed to significant particulate debris. Metal mesh, particularly when made from stainless steel or aluminum, provides enhanced durability and heat resistance, making it a popular choice across various sectors.
Advantages of mesh filters typically include their high flow rates, allowing fluids to pass through quickly, and their effectiveness in capturing larger particles. They are frequently used where precise particle size separation is needed but extremely fine filtration is not the primary requirement. For lighter applications, many mesh filters are also designed for easy cleaning and reusability, contributing to their cost-effectiveness over time.
Despite their versatility, mesh filters do come with certain limitations. Their porous structure, while great for flow, can sometimes lead to clogging, especially when dealing with high concentrations of fine particulates or sticky substances like grease. The overall durability and efficacy can also be highly dependent on the chosen material; for example, plastic mesh may become brittle over time or degrade with exposure to high temperatures or certain chemicals.
The Power of Stainless Steel in Filtration
Stainless steel, as a material, brings a host of powerful advantages to the world of filtration, making it a premium choice for many demanding applications. Unlike a structural type, stainless steel is an alloy known for its exceptional properties that enhance any filter it comprises. Its inherent strength and resilience mean that filters made from stainless steel offer a robust solution that stands the test of time and challenging environments.
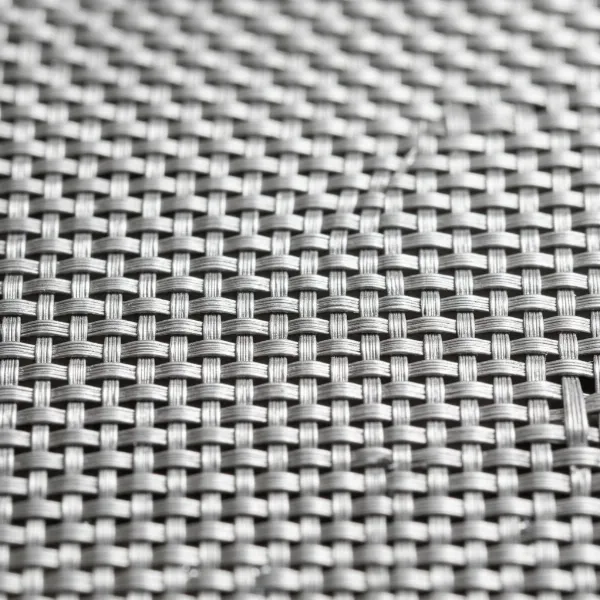 Close-up of a tightly woven stainless steel mesh filter showing its intricate and durable structure for effective filtration.
Close-up of a tightly woven stainless steel mesh filter showing its intricate and durable structure for effective filtration.
One of the foremost benefits of stainless steel filters is their outstanding durability and extended lifespan. They are highly resistant to wear and tear, reducing the need for frequent replacements, which translates into significant long-term cost savings. Furthermore, stainless steel exhibits superior corrosion resistance, particularly grades like 304 and 316, which are well-suited for environments exposed to moisture, chemicals, or chlorides. This resistance prevents rust and degradation, maintaining the filter’s structural integrity and performance over many years.
Heat resistance is another critical advantage, with stainless steel filters maintaining their structural integrity at temperatures far exceeding those that would compromise plastic alternatives. This makes them ideal for hot liquid applications, such as in electric kettles or brewing equipment. From a hygiene perspective, stainless steel is non-reactive and does not leach harmful chemicals into filtered substances, making it a safe choice for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries. Its smooth surface also resists the growth of microorganisms, and most stainless steel filters are dishwasher safe and easy to clean, promoting excellent sanitation and reusability.
However, the premium quality of stainless steel typically comes with a higher upfront cost compared to filters made from less durable materials like plastic. Additionally, stainless steel filters can be heavier, which might be a consideration in some lightweight applications. It’s important to remember that “stainless steel filter” encompasses various structural types, including mesh, perforated sheets, and sintered metal, each optimized for different levels of filtration and strength.
Direct Comparison: Mesh vs. Stainless Steel – Where They Differ and Overlap
When evaluating filter types, the choice often comes down to balancing material properties with structural design. Understanding how mesh filters, regardless of material, compare to filters specifically leveraging stainless steel’s attributes is crucial for optimal performance.
Filtration Effectiveness and Particle Capture
Table is empty.The ability to capture particles is a primary concern for any filter. Generic mesh filters, with their woven structure, are generally highly effective at trapping larger particles, making them suitable for applications requiring coarse to medium filtration. The specific pore size dictates the minimum particle size that can be retained, and this can vary greatly depending on the weave and material. For instance, a fine nylon mesh can capture small particles but may be delicate.
Stainless steel, as a material, allows for exceptional precision in filter manufacturing. Stainless steel mesh filters can be woven incredibly finely, enabling them to capture very small particles while maintaining durability. Furthermore, stainless steel is also used to create sintered filters, which bond metal powder particles to form a porous structure capable of ultra-fine filtration, often down to 0.1 microns. This makes stainless steel an unparalleled choice when high-purity filtration is paramount, far exceeding the capabilities of most non-metallic mesh filters.
Durability and Lifespan
The longevity of a filter is heavily influenced by its material. While mesh filters made from plastic or aluminum offer reasonable durability for light use, they are often susceptible to brittleness, corrosion, or deformation over time, especially with exposure to heat or harsh chemicals. Plastic mesh, for example, may degrade and require frequent replacement.
In contrast, stainless steel filters, whether mesh or another form, boast exceptional durability. Their inherent strength and corrosion resistance mean they can withstand aggressive operating conditions, high pressures, and chemical exposure without losing integrity. This robust nature translates into a significantly longer lifespan, reducing maintenance frequency and overall replacement costs. The material’s resilience ensures consistent performance even in challenging environments.
Heat and Chemical Resistance
Heat and chemical resistance are critical factors, especially in culinary and industrial settings. Plastic mesh filters are generally limited by temperature, softening or leaching chemicals at higher heat levels. They can also be degraded by certain solvents or acidic substances, making them unsuitable for many applications.
Stainless steel filters, conversely, offer superior resistance to both high temperatures and a wide range of chemicals. They maintain their structural integrity at extreme temperatures, some industrial-grade stainless steel filters can withstand up to 800°C, and are resistant to oxidation, acids, and alkalis. This chemical inertness prevents unwanted reactions and ensures the purity of the filtered substance, a crucial aspect in food processing and pharmaceutical applications.
Maintenance and Cleaning
Ease of maintenance directly impacts the practicality and long-term cost of a filtration system. Many mesh filters, particularly those made from durable materials like stainless steel or aluminum, are designed for reusability. They can often be cleaned through simple methods such as rinsing, back-flushing, or even dishwasher cycles. This reusability reduces waste and the ongoing expense of disposable filters.
However, the intricate weave of some mesh filters can make them challenging to clean effectively, especially when trapping sticky substances like grease or very fine particles that embed deeply. Regular cleaning is essential to prevent clogging and maintain filtration efficiency. Stainless steel filters generally excel in this area; their smooth, non-porous surfaces prevent particle adhesion and can be thoroughly sanitized, ensuring hygienic operation.
Cost and Value
The initial investment for a filter can vary significantly. Generic mesh filters, especially those made from plastic, tend to have a lower upfront cost, making them attractive for budget-conscious consumers or temporary applications. However, their shorter lifespan and potential for frequent replacement can lead to higher long-term expenses.
Stainless steel filters, while typically requiring a higher initial outlay, offer superior long-term value. Their unparalleled durability, reusability, and reduced need for replacement result in lower overall ownership costs. The extended service life also minimizes system downtime and maintenance efforts, providing excellent value over many years of operation.
Applications: Where Each Filter Type Shines
The ideal filter choice is often dictated by its intended application and the specific demands of the environment. Both mesh and stainless steel filters have distinct strengths that make them suitable for various uses.
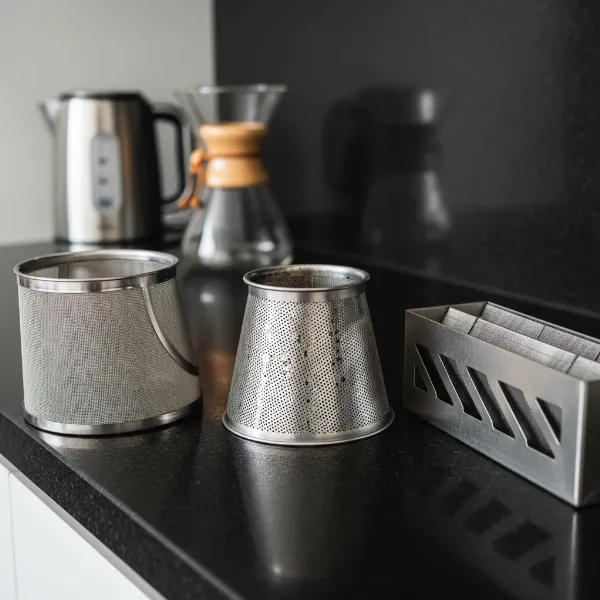 Various kitchen appliance filters, including mesh and stainless steel types, showcasing their design for different culinary uses.
Various kitchen appliance filters, including mesh and stainless steel types, showcasing their design for different culinary uses.
In kitchen appliances, stainless steel mesh filters are ubiquitous. In Electric Kettles, they effectively catch limescale, ensuring a clean pour. Coffee makers often utilize stainless steel mesh to filter coffee grounds, allowing for rich, sediment-free brews. For range hoods, the comparison often shifts to mesh versus baffle filters, both frequently made of stainless steel or aluminum. Stainless steel mesh filters in range hoods are praised for capturing finer airborne grease particles and operating more quietly, while stainless steel baffle filters are preferred for heavy cooking due to their ability to capture larger grease droplets and act as a fire barrier.
For water filtration, stainless steel mesh filters are highly valued for their durability and corrosion resistance, used in residential and commercial systems to remove sediment. When ultra-fine filtration is required, sintered stainless steel filters are often deployed due to their microscopic pore sizes, ensuring high purity. In industrial applications, stainless steel filters, in various forms including mesh and sintered, are indispensable. They are found in petrochemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage production, and wastewater treatment, where their chemical resistance, high temperature tolerance, and mechanical strength are paramount.
Choosing the Right Filter: Key Considerations
Selecting the perfect filter requires a thoughtful evaluation of several factors to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. The “best” filter isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution but rather the one that most appropriately meets your specific needs.
First, consider the application and purpose. Are you filtering water, air, oil, or food? What kind of contaminants are you trying to remove? For example, a filter for a home coffee maker will have different requirements than a filter for a commercial chemical plant. Next, assess the particle size you need to capture. Coarser mesh filters are adequate for larger debris, while finer mesh or sintered stainless steel filters are necessary for microscopic impurities.
Flow rate requirements are also crucial; some applications demand high fluid or air flow, which certain filter types (like coarse mesh) handle better than others (like dense sintered filters). Operating conditions such as temperature, pressure, and exposure to corrosive chemicals will heavily influence the material choice, with stainless steel being the superior option for harsh environments. Finally, evaluate your budget and maintenance preferences. While stainless steel filters may have a higher initial cost, their reusability and longevity can offer significant long-term savings compared to cheaper, disposable alternatives that require frequent replacement.
> “While basic mesh filters offer a pragmatic solution for many everyday filtration needs, the material choice elevates performance significantly. Stainless steel, in particular, transforms a simple mesh into a highly durable, hygienic, and long-lasting component critical for demanding environments and consumer safety.” — Dr. Anya Sharma, Filtration System Engineer.
Conclusion
The distinction between mesh filters and stainless steel filters highlights a fundamental aspect of filtration: the synergy between design and material. While “mesh” defines a filter’s interwoven structure, “stainless steel” speaks to the exceptional qualities of its composition. Stainless steel mesh filters embody the best of both worlds, combining the effective particle capture of a mesh design with the unparalleled durability, corrosion resistance, and hygienic properties of stainless steel. This makes them a superior choice for a myriad of applications, from ensuring clean drinking water and perfectly brewed coffee to maintaining industrial process purity.
Whether you’re looking for a filter that can withstand high temperatures, resist corrosive chemicals, or simply offer a long-lasting and reusable solution, understanding the benefits of stainless steel as a filter material is paramount. Investing in the right filter technology means less frequent replacements, improved performance, and a safer, cleaner environment. What specific filtration challenge are you looking to solve in your home or industry today?
Frequently Asked Questions
Are stainless steel mesh filters better than plastic filters?
Generally, yes. Stainless steel mesh filters offer superior durability, heat and chemical resistance, and do not leach harmful chemicals, especially at high temperatures. While plastic filters are cheaper upfront, stainless steel filters are more hygienic, reusable, and provide better long-term value and performance.
How often should I clean my stainless steel filter?
The cleaning frequency depends heavily on the filter’s application and usage. For kitchen appliances like kettles or range hoods, cleaning every 1-3 months or more frequently with heavy use is often recommended to prevent mineral buildup or grease accumulation and maintain optimal performance. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific instructions.
Can I use a mesh filter for very fine particles?
Standard mesh filters are generally best for capturing larger particles and debris while allowing good flow. For very fine particles, especially those requiring filtration down to micron levels, a very fine stainless steel mesh or a sintered stainless steel filter is often a more effective choice due to its denser and more uniform pore structure.
What are the benefits of stainless steel filters in home use?
In home use, stainless steel filters offer numerous benefits including enhanced durability and longevity, resistance to rust and corrosion, and the ability to withstand high temperatures. They are also non-reactive, ensuring filtered substances remain pure, and are typically easy to clean and reuse, contributing to a more sustainable kitchen.